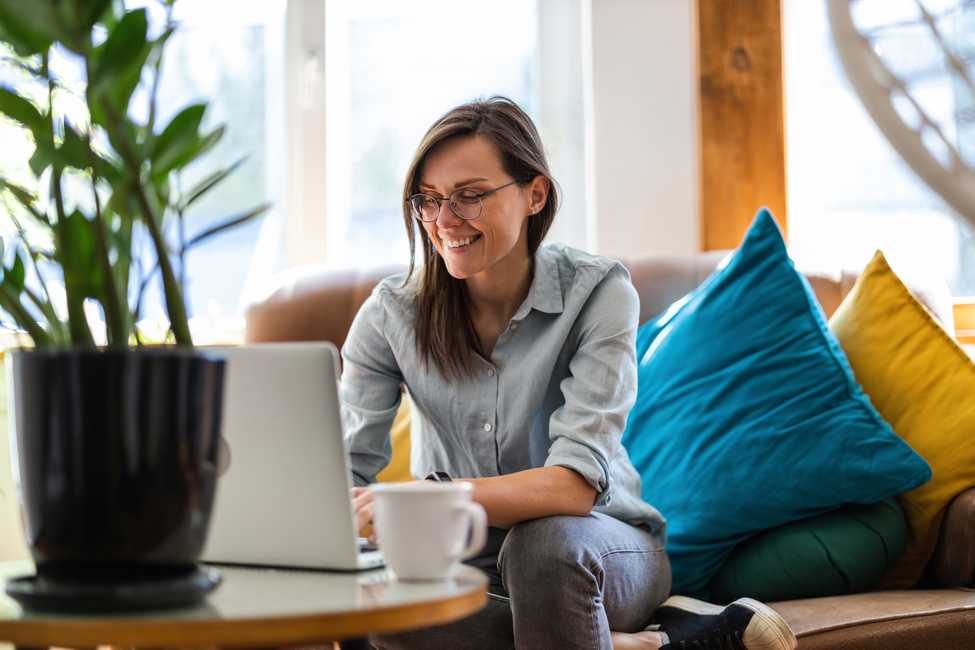
Help
If you need assistance, please reach out using the form below. Or you can take a look at our Frequently Asked Questions and Resources below.

Frequently Asked Questions
At the company level, our debt relief benefit is a unique payroll code (new line item) that diverts funds to us. On behalf of employees, we remit monthly payments to Canadian student loan and residential mortgage lenders.
We operate independently of savings plan providers.
Debt relief benefits are an optional, taxable employee benefit with competitive and reasonable annual software subscription rates. Small businesses can offer debt relief for as little as $500.
Employers may or may not cover monthly transaction fees.
The debt relief component is prepaid for employers who enable savings contributions to become debt payments.
As of 2018, about 6 in 10 young people left post-secondary with student loans to repay.
Surveys indicate 25% of working Millennials are still in student loan repayment.
Mortgage holders will outnumber student loan holders in most workplaces.
Because the employer cost of employee financial stress is greater than the cost of these benefits.
Debt relief benefits empower employees and reduce their financial stress with extra monthly payments on their debt.
Debt relief benefits are flexible financial solutions that support employees’ financial priorities.
Originally designed to repurpose savings plan contributions into debt payments, employers now find multiple ways of helping employees save time and money repaying a student loan or residential mortgage.
